Lecture #12: Reflection and refraction
Computer graphics in Game development
Ivan Belyavtsev
21.02.2020
Reflection
“Reflection” experiment
TODO
- Add reflection for reflective materials
“Reflection” experiment
Reference
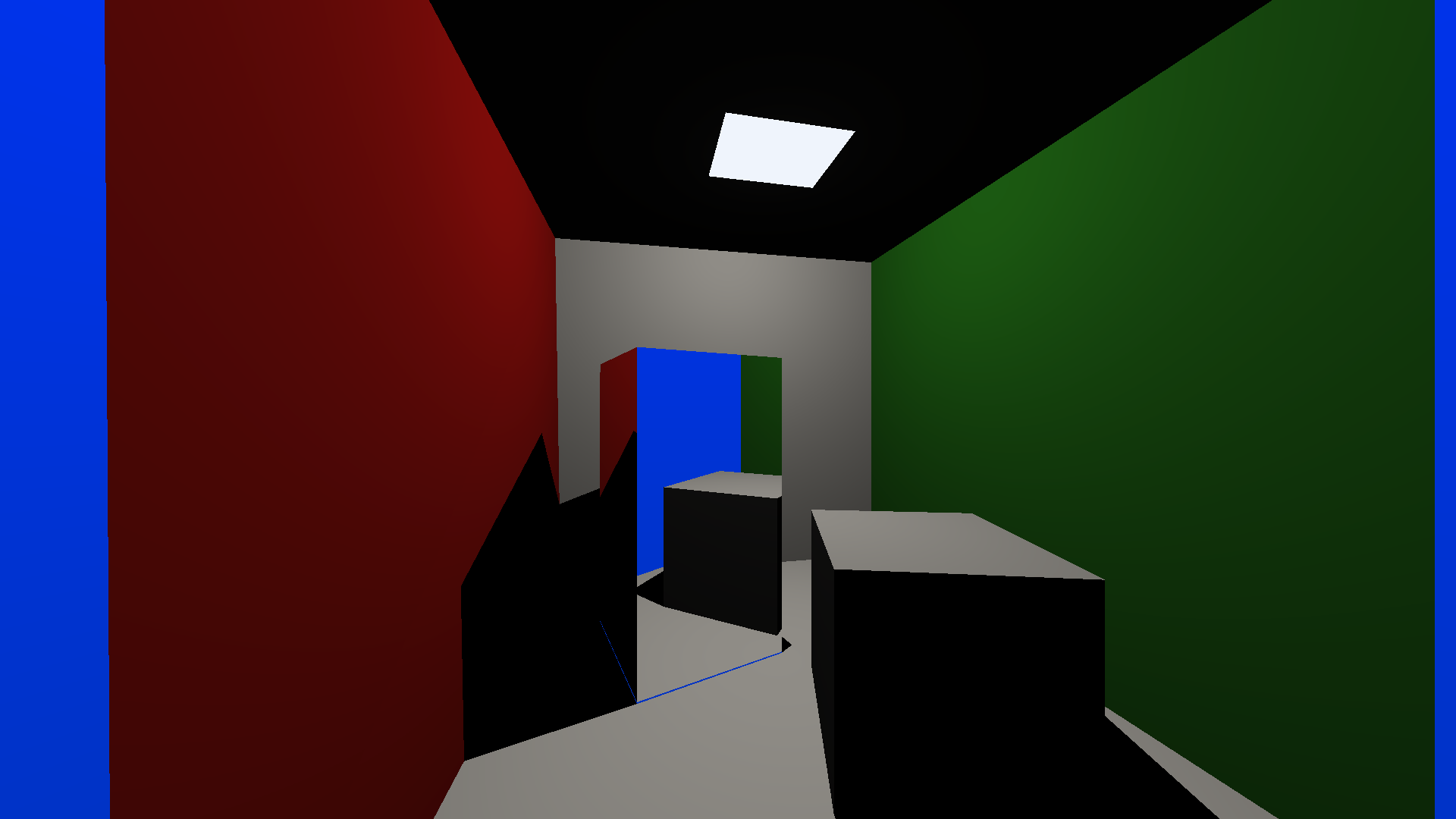
“Reflection” experiment
What is the new knowledge?
- How to recast usual rays
- How to implement reflections
- How to avoid stack overflow error
Refraction
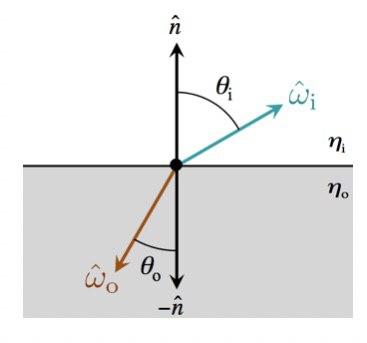
Snell’s law
\[\frac{\sin(\theta_o)}{\sin(\theta_i)}=\frac{v_o}{v_i}=\frac{n_i}{n_o}\]
Fresnel equations
\(T\) - Refraction ability \(R\) - Reflection ability
\[T+R = 1\]
Fresnel equations
Reflectance
\(R_s\) - reflectance for s-polarized light
\(R_p\) - reflectance for p-polarized light
\[R = \frac{R_s + R_p}{2}\]
Fresnel equations
S-polarized light
\[R_s = \biggl|\frac{n_1\cos{\omega_i}-n_2\cos{\omega_o}}{n_1\cos{\omega_i}+n_2\cos{\omega_o}}\biggl|^2\]
Fresnel equations
P-polarized light
\[R_p = \biggl|\frac{n_1\cos{\omega_o}-n_2\cos{\omega_i}}{n_1\cos{\omega_o}+n_2\cos{\omega_i}}\biggl|^2\]
“Refraction” experiment
TODO
- Implement refractions for needed materials
“Refraction” experiment
Reference
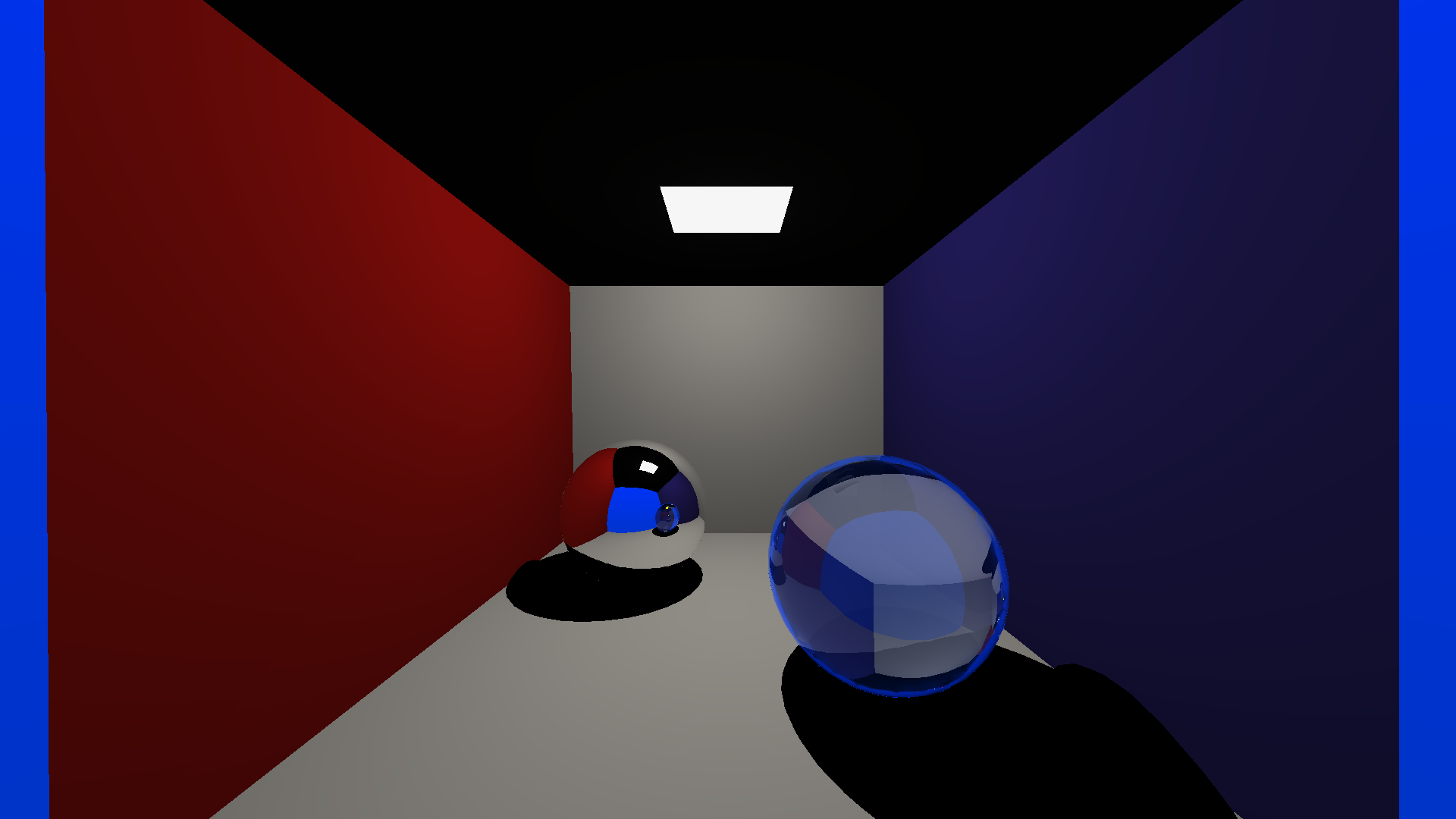
“Refraction” experiment
- How to apply Snell’s laws to refractions
- How to apply Fresnel equations to refractions
References
1. McGuire M. The graphics codex. 2.14 ed. Casual Effects, 2018.