Lecture 08: Lighting and shadows
Computer graphics in Game development

Ivan Belyavtsev
10.06.2022
Current result vs rasterizer
Rendering equation
\[\scriptsize{L_o(X, \vec{\omega_o}) = L_e(X, \vec{\omega_o}) + \int_S L_i(X, \vec{\omega_i}) f_{X,\vec{n}}(\vec{\omega_i}, \vec{\omega_o}) |\vec{\omega_i} \cdot \vec{n} | d{\omega_i}} \]
where \(X\) is a position on the object or surface,
\(\vec{\omega_o}\) is a direction toward the eye or camera,
\(L_o(X, \vec{\omega_o})\) is all outgoing light from the position,
\(L_e(X, \vec{\omega_o})\) is emitted light [1]
Rendering equation
\[\scriptsize{L_o(X, \vec{\omega_o}) = L_e(X, \vec{\omega_o}) + \int_S L_i(X, \vec{\omega_i}) f_{X,\vec{n}}(\vec{\omega_i}, \vec{\omega_o}) |\vec{\omega_i} \cdot \vec{n} | d{\omega_i}} \]
where \(\vec{n}\) is normal to surface at \(X\) position,
\(S\) is a unit hemisphere among \(\vec{n}\) with center in \(X\),
\(L_i(X, \vec{\omega_i})\) is a light coming from \(\vec{\omega_i}\) direction,
\(f_{X,\vec{n}}(\vec{\omega_i}, \vec{\omega_o})\) is the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) [1]
Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
![fig: From: [2]](img/brdf_example.jpg)
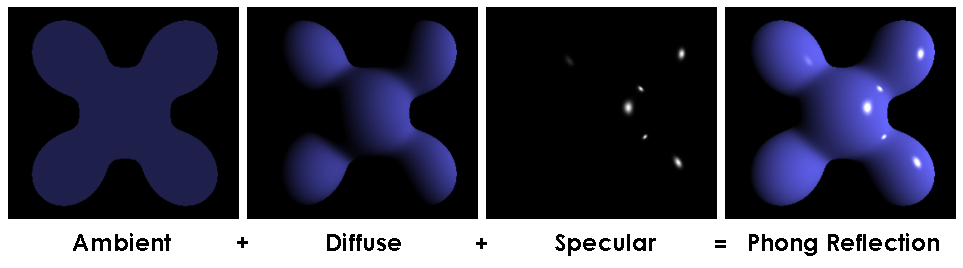
Phong shading
\[\small{L(\vec{P}) = Ka + \sum_{lights}{[Kd\vec{N} \cdot \vec{L} + Ks(\vec{V} \cdot \vec{R})^{Ns}]}}\]
where \(\small{\vec{R} = 2(\vec{N} \cdot \vec{L})\vec{N}−\vec{L}}\) [3]
Lambertian shading
\[L_d = k_dI\max(0, \vec{n}\cdot\vec{l})\]
where \(L_d\) - diffusely reflected light,
\(k_d\) - material’s diffuse coefficient,
\(\vec{n}\) - surface normal,
\(\vec{l}\) - direction toward the light [4]
Lab: 2.03 Lambertian shading
- Add light information to
lightsarray ofray_tracing_renderer - Adjust
closest_hit_shaderofraytracerto implement Lambertian shading model
Shadow rays idea
Before adding the light source to the final point on the point \(X\), we should cast a ray from the point \(X\) towards the light source. If any object occludes the shadow ray, the point \(X\) is on shadow and the light should not be added the light source
Shadow rays
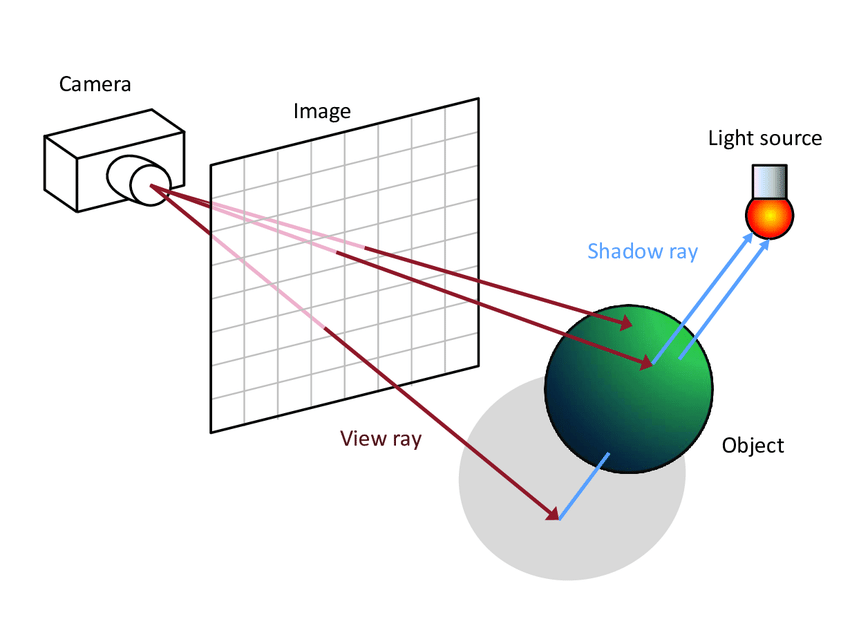
Shadow rays tips
- Intersection with any geometry farther than light source doesn’t occlude the light source. To skip such object cast the ray with \(t_{max}\) less than distance from \(X\) to the light source
- To avoid self-intersection with the triangle owning \(X\), use \(t_{min}\) more than 0
- One intersection is enough to find an occlusion - use an AnyHit shader
Lab: 2.04 Shadow rays
- Adjust
trace_raymethod ofraytracerto useany_hit_shader - Initialize
shadow_raytracerinray_tracing_renderer - Define
any_hit_shaderandmiss_shaderforshadow_raytracer - Adjust
closest_hit_shaderofraytracerto cast shadows rays and to ignore occluded lights